The medication circuit in health care institutions
According to the "Légifrance" website:
the decree of 31 March 1999 on the prescription, dispensing and administration of medicines subject to the regulation of poisonous substances in health establishments, inter-hospital unions and medico-social establishments with an in-house pharmacy mentioned in Article L. 595-1 of the public health code... . Health establishments must therefore comply with very specific standards in the distribution of medicines.
This article of the Public Health Code separates the drug circuit within a healthcare establishment into three distinct areas:
- Medical area
- Pharmaceutical area
- Nursing area
The medication circuit begins in the care units, more precisely from the moment the doctor writes a prescription which will be sent to the establishment's pharmacy. This prescription must clearly indicate the duration of the treatment, the identification of the care unit and the contact information for the prescriber (the doctor).
Once the prescription has been written and signed by the doctor, it is sent to the hospital pharmacy where it will be analysed, processed and archived for a period of three years.
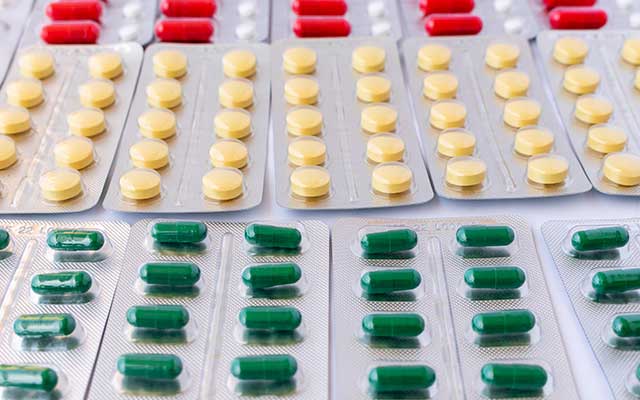
During the preparation of the medicines by the pharmacy, it provides information on the use of the medicine if necessary. Once the preparation is complete, the pharmacy arranges for the medicines to be transported to the ward in locked trolleys or containers.
Once on the ward, the nurses are responsible for administering the medicines to the patients, checking in advance how they are to be administered (weekly PDA).
If not all the medicines are administered to the patients on the ward, the facility should provide a storage space, which may be a locked room and/or storage cabinets.
The aim is to keep control of the medicines outside the pharmacy and thus avoid any theft.
 Francais
Francais 
 Cart
Cart Quote
Quote